Posted: November 04, 2024 by: jiandan
What Is PCB Color?
The color we see on the PCB is actually the color of the solder resist layer, and the color of the solder resist layer mainly depends on the color of the solder mask.The most common PCB colors in the market include green, blue, black, white , red , and purple. PCB of different colors may have variations in the manufacturing process; for example, the production process for black solder resist layers is relatively complex, resulting in higher costs.
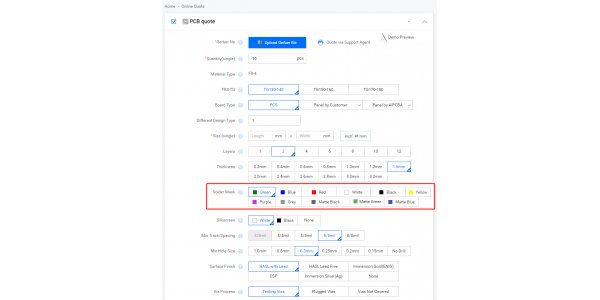
AiPCBA provides 11 PCB solder mask colors, including green, blue, red, white, black, yellow, purple, grey, matte black, matte green, and matte blue. These options can meet various PCB environmental and performance requirements, allowing you to choose the PCB color that best suits your needs.
Types of PCB Colors
The most widely used and common PCB color in the current market is green, followed by black, white, red, pink, blue, and others. The reason for the availability of various colors in PCBs is as follows:
- Using different colors helps to distinguish between different stages of the product
Initially, red PCBs represented the first version or draft, yellow PCBs were used for validation versions, and green or blue PCBs indicated the final version.
However, nowadays, such distinctions are not as strictly adhered to. Typically, the industry tends to use a consistent color, employing the same solder mask color to reduce the cost associated with changing production lines.
- Different industries have varying requirements for PCB performance
For example, the PCB for LED lights is typically white, as white can reflect light, increase brightness, and reduce heat absorption.On the other hand, black PCB boards are commonly used in dot matrix displays. Black helps minimize reflections and diffuse light, improving pixel contrast and enhancing the overall display effect of the screen.
- Engineers may have different personal color preferences
Many hobbyist electronics enthusiasts and some artistic PCB designers may consider the appearance of the PCB, aiming for an aesthetic and pleasing look. Therefore, they might choose pink or purple PCBs.
PCB-Color-Codes-and-Differences
Here are introductions to the 7 types of PCB color codes and differences.
- Green PCB
The green PCB is the most common color for PCB boards, offering good visibility and recognition. Additionally, the production process for the green solder resist layer is relatively mature, resulting in lower costs, making it widely applied.
- Red PCB
The red PCB has a strong visual impact, providing clear contrast for traces, planes, and blank areas. It is commonly used in high-end or specialized electronic products.However, the production process for the red solder resist layer is relatively complex, resulting in higher costs, and its application scope is relatively limited.
- Black PCB
Black PCBs are often used in dot matrix displays, mid-to-high-end, or flagship products because black can reduce reflection and diffuse light, improving pixel contrast and enhancing screen display performance.In some electronic devices where electromagnetic interference needs to be minimized, black PCBs can effectively absorb and shield electromagnetic waves, enhancing the device's anti-interference capabilities.Generally, the light board of traffic signal lights uses a black PCB to achieve a black background.

However, the surface traces on a black PCB are mostly obscured, which increases the difficulty of research and development, maintenance, and debugging. Moreover, black PCBs pose the highest difficulty for drilling holes, leading to a lower yield compared to PCBs of other colors. Consequently, the cost is relatively higher.
For confidentiality reasons, some manufacturers opt for black PCB boards since the wiring is less visible, introducing a level of difficulty for reverse engineering. For instance, many PCBs in Android embedded systems use black PCBs.
- Blue PCB
Blue PCBs contain a small amount of titanium, which can enhance solder joint reliability. In positions where high-frequency signal lines are connected, blue titanium solder is often used to ensure quality.Blue PCBs are commonly employed in LCDs because they do not produce sharp contrasting edges and bright background colors.

- White PCB
White PCBs are typically used in LED boards. The white color provides reflectivity, enhancing brightness and reducing heat absorption. Additionally, white PCBs can increase the brightness of the PCB and contribute to an overall aesthetic appeal.

- Yellow PCB
Yellow PCBs were more commonly used in the past to quickly meet cleanliness and visibility requirements for certain applications. However, due to the lower contrast between traces and silk screen, they are not as widely used today.
Why Is Most Circuit Board Color Green?
Currently, there are various colors of PCBs such as red, blue, purple, black, white, etc., but green PCBs are the most common. This is mainly because using green PCBs offers the following advantages:
- Lower Cost
Green PCBs are one of the most widely used types, leading to lower production costs on a large scale. They are relatively more economical and cost-effective, making green a popular choice among many manufacturers.
- Clear Contrast With Impurities
During PCB manufacturing, it is necessary to remove impurities from the PCB, and green PCBs show impurities more clearly compared to PCBs of other colors.
- Beneficial For Optical Positioning Calibration
PCB fabrication processes involve SMT soldering, which includes tinning and final AOI checks. These processes require optical positioning calibration, and the green background provides the best recognition effect for instruments.
- Best Visual Effects In Yellow Light Rooms
During electronic product manufacturing processes, some procedures require exposure to yellow light. According to optical principles, green PCBs have the best visual effects in yellow light rooms, making it easier to observe the production of electronic products.
- Facilitates Workers' Observation Of the Circuit Board
Due to current manufacturing processes, PCB quality inspection still relies on manual visual inspection. Green is the least harmful to the eyes when workers continuously observe the board under strong light.
- Relatively Safe And Environmentally Friendly
Blue and black inks used in PCBs contain cobalt and carbon elements, which may lead to short circuits when powered. Green PCBs have a lower likelihood of short circuits. When used in high-temperature environments, green PCBs generally do not release toxic gases.
HOW to choose the right color for your PCB?
- Manufacturing Cost
The PCB color can impact manufacturing costs. Different colors require different solder mask inks, and there may be variations in the manufacturing process, leading to different costs.For example, metal PCBs in colors like gold and silver typically incur higher manufacturing costs. Therefore, when choosing PCB color, it's essential to consider the product's positioning and cost budget.
If you want to know the cost differences associated with using different solder mask colors for your PCB, you can upload Gerber files on our PCB quotation page to get a quote.
- Soldering Convenience
In PCB manufacturing, soldering is a crucial step, and the color of the PCB can have a certain impact.
Generally, PCBs with dark backgrounds can better absorb the light generated during soldering, making solder joints clearer. For example, green color can enhance the visibility of solder joints for soldering personnel, reducing the risk of soldering errors.
- EMI Compatibility
Some dark-colored PCBs can reduce the EMI of the PCB, contributing to improved electromagnetic compatibility of the product.However, it's important to note that color is just one factor in addressing electromagnetic compatibility issues. It needs to be considered in conjunction with circuit design, component selection, and circuit layout.
- Heat Dissipation
For instance, black PCBs can absorb more heat, contributing to improved heat dissipation. However, if too much heat is absorbed in high-temperature environments, it may adversely affect heat dissipation.
Therefore, when choosing PCB colors, it's essential to consider the actual application scenario of the product.
- Repairability
Black PCBs may obscure traces, increasing the difficulty of research, development, and debugging. In contrast, green PCBs or red PCBs make it easier to observe components and circuit traces, reducing the difficulty of repairs.
AiPCB offers 11 resist layer colors, including green, blue, red, white, black, yellow, purple, grey, matte black, matte green, and matte blue. These options cater to various PCB environments and performance requirements, allowing you to choose the color that suits your needs.