Posted: May 26, 2022 by: Bonnie
Other factors in the conventional manufacturing process may affect manufacturability, such as the type of raw materials, the form of raw materials, dimensional tolerances, and secondary processing such as finishing. According to various types of manufacturing processes, guidelines are set for DFM practice. These DFM guidelines help to accurately define various tolerances, rules and routine manufacturing inspections related to DFM, and ultimately achieve the purpose of reducing various costs.
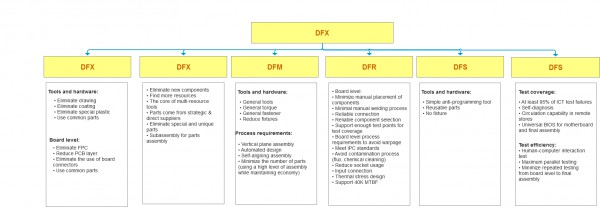
DFM is an important branch of DFX:
- DFX (Design for Excellence or Design for X) covers a lot of content, involving various stages of product development, such as:
- DFA (Design for Assembly)
- DFM (Design for Manufacturing)
- DFT (Design for Test)
- DFE (Design for Electro-Magnetic Interference)
- DFC (Design for Cost)
- DFC (Design for Component)
It can be seen that DFM is bidirectional, and product development and technology need to be put into it, and parallel development is indispensable. DFM is not a simple technology. In a sense, it is more like an idea, included in all aspects of product realization.
Today's DFM is the core technology of concurrent engineering, because design and manufacturing are the two most important links in the product life cycle. Concurrent engineering is to consider the manufacturability and assembleability of the product when starting the design. So DFM is the most important support tool in concurrent engineering. The key to it is the technical analysis of design information, evaluation of manufacturing rationality, and suggestions for improving design.
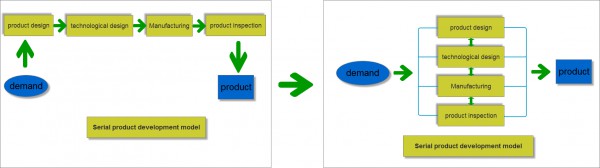
The evolution of DFM framework and operation mode.
PCB design, as the most important process from logic to physical implementation, DFM design is an important aspect that cannot be avoided. In PCB design, what we call DFM mainly includes: device selection, PCB physical parameter selection and PCB design details.
In general, device selection mainly refers to the selection of devices that are more advantageous in terms of procurement, processing, and maintenance. For example: try to use SOP devices instead of BGA devices; use devices with large pitch and do not use fine pitch devices; try to use conventional devices instead of special devices. The DFM selection of the device, as a PCB designer, needs to be negotiated with the procurement engineer, hardware engineer, process engineer, etc.
The main part of the physical parameters of PCB design is mainly determined by the PCB designer. Mainly include: setting of board thickness aperture ratio, line width spacing, stacking design, pad aperture, etc. This requires PCB designers to have an in-depth understanding of the PCB manufacturing process and manufacturing methods, understand the processing parameters of most board factories, and then set the physical parameters in combination with the actual situation of the single board, try to increase the PCB production process window, and use the most Mature processing technology and parameters reduce processing difficulty, improve yield, and reduce the cost and cycle of PCB production in the later stage.
Many situations in PCB design details have a lot to do with the level and experience of design engineers. Such as: device placement, spacing, wiring processing, copper processing, etc. These parameters require long-term accumulation of multiple projects to obtain. Generally speaking, professional design is exposed to more requirements of PCB board factories and welding processing plants, so their design parameters can generally meet the requirements of most board factories, rather than only meeting the specific cost requirements of a certain factory.
We need to get things right at once in the early stages of the product life cycle! The figure below gives an analysis of the degree of influence of each character.
From the previous analysis, DFM manufacturability design has the following values, and the advantages are summarized as follows:
• Shorten the product development cycle and win time for the product to be quickly brought to market;
• Reduce manufacturing costs and improve product competitiveness;
• Improve the overall reliability of the product;
• Conducive to the standardization and automation of the production process and improve production efficiency;
• Facilitates technology transfer, simplifies product transfer process, and strengthens collaboration and communication between companies;
• Improve the competitiveness of product after-sales.
DFM application range:
- PCB fabrication
- For integrated circuits (IC)
- For CNC machining
Development of DFM
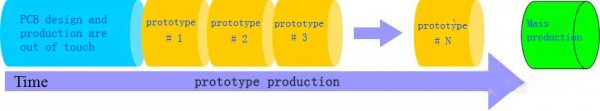
Traditional manufacturability design, PCB design is out of touch with PCB production, it needs multiple rounds of trial production to determine the existing manufacturability problems, and then in turn guide the design to solve the manufacturability design problems before the batch.
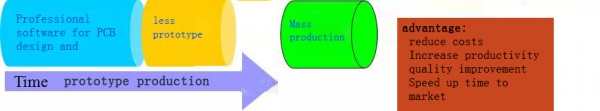
The process of parallel design after DFM reconstruction.
From the current development point of view, DFM has experienced the early, early, and middle stages, and has experienced software and digitalization. Currently, it is gradually moving towards automation and intelligence. As the most dynamic component of product design in the future, DFM must cooperate with artificial intelligence and experts. Systems and other technologies are combined to support the comprehensive and parallel requirements of modern product design. Follow the information exchange standard and adopt the results of information exchange standardization to achieve the integration between systems in the product design process.
