It is through a semiconductor manufacturing process such as oxidation, photolithography, diffusion, epitaxy, and aluminum vaporization. It integrates semiconductors, resistors, capacitors and other components required to form a circuit with certain functions and the connecting wires between them in a small piece of silicon. On-chip, then soldered electronics packaged in a tube and shell. Its package shell has a variety of forms such as round shell, flat or dual in-line.
1. Characteristics
The aforementioned integrated circuit in which a circuit is manufactured on the surface of a semiconductor chip is also referred to as a thin-film integrated circuit. Another type of thick-film hybrid integrated circuit is a miniaturized circuit composed of independent semiconductor devices and passive components integrated into a substrate or circuit board.
2. Classification
Integrated circuits, also known as ICs, can be divided into three categories: analog integrated circuits, digital integrated circuits, and digital / analog hybrid integrated circuits according to their functions and structures.
2. 2 Production process
Integrated circuits can be divided into semiconductor integrated circuits and film integrated circuits according to the manufacturing process.
Film integrated circuits are classified into thick film integrated circuits and thin film integrated circuits.
3. IC Types
Ball contact array, one of the surface mount packages.
Flat four-lead package with cushion.
3) C- (ceramic)
Symbol for ceramic package. For example, CDIP stands for ceramic DIP. It is a mark often used in practice.
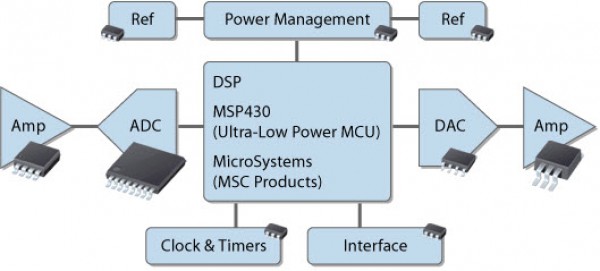
Glass sealed ceramic dual in-line package for ECL RAM, DSP (Digital Signal Processor) and other circuits.
One of the surface-mount packages is a sealed ceramic QFP, which is used to package logic LSI circuits such as DSPs.
On-chip chip packaging is one of the bare chip placement technologies.
Flat package on both sides. It is another name for SOP (see SOP).
Another name for ceramic DIP (including glass seal) (see DIP).
Another name for DIP (see DIP). European semiconductor manufacturers often use this name.
Dual in-line package. One of the plug-in packages, the pins are drawn from both sides of the package, and the package materials are plastic and ceramic.
Small form factor package on both sides. Another name for SOP (see SOP). Some semiconductor manufacturers use this name.
Double-sided pin carrier package. One of TCP (Tape Loaded Encapsulation).
Ibid. The Japanese Electronic Machinery Industry Association named DTCP (see DTCP).
Flat package. One of the surface mount packages. Another name for QFP or SOP (see QFP and SOP). Some semiconductor manufacturers use this name.
Flip the chip. One of the bare chip packaging technologies,
The center of the small pin is QFP. Usually refers to QFP (see QFP) with a pin-to-center distance of less than 0.65mm. Some conductor manufacturers use this name.
Another name for BGA by Motorola, USA (see BGA).
Four-lead flat package with guard ring.
Indicates a mark with a heat sink. For example, HSOP means SOP with heat sink.
Surface mount PGA. Usually PGA is a plug-in package with a lead length of about 3.4mm.
J-shaped chip carrier. Refers to other names for windowed CLCC and windowed ceramic QFJ (see CLCC and QFJ). The name adopted by some semiconductor manufacturers.
Leadless chip carrier. Refers to a surface mount package where the four sides of the ceramic substrate have only electrode contact and no leads. It is a package for high-speed and high-frequency ICs, also known as ceramic QFN or QFN-C (see QFN).
Contact display package. That is, a package with an array of state electrode contacts is made on the bottom surface. Just plug in the socket during assembly.
On-chip lead package. One of the LSI packaging technologies,
Thin QFP. Refers to the QFP with a package body thickness of 1.4mm, which is the name used by the Japan Electromechanical Industry Association based on the new QFP outline specifications.
Ceramic QFP one. Aluminum nitride for package substrates has a base thermal conductivity that is 7-8 times higher than alumina, and has good heat dissipation.
Multi-chip components. A package in which a plurality of semiconductor bare chips are assembled on a wiring substrate.
Small flat package. Alternative name for plastic SOP or SSOP (see SOP and SSOP). The name adopted by some semiconductor manufacturers.
A classification of QFP according to JEDEC (United States Electronic Equipment Council) standards.
A QFP package developed by Olin Corporation. The substrate and cover are made of aluminum and sealed with an adhesive.
Another name for QFI (see QFI) is often called MSP in the early stages of development. QFI is a name prescribed by the Japan Electromechanical Industry Association.
A mark indicating a plastic package. For example, PDIP means plastic DIP.
Bump display carrier, another name for BGA (see BGA).
Moulded resin seal bump display carrier. The name Motorola uses for molded resin-sealed BGAs (see BGA).
Plastic flat package. Another name for plastic QFP (see QFP). The name adopted by some LSI manufacturers.
Display pin package. One of the plug-in packages has vertical pins on the bottom surface arranged in a display. The packaging substrate is basically a multilayer ceramic substrate.
Ballast package. Refers to a ceramic package with a socket. The shape is similar to DIP, QFP, QFN.
Leaded plastic chip carrier. One of the surface mount packages.
Sometimes it is another name for plastic QFJ, sometimes it is another name for QFN (plastic LCC) (see QFJ and QFN).
Four-sided thick-body flat package. A type of plastic QFP. In order to prevent the package body from breaking, the QFP body is made thicker (see QFP). The name adopted by some semiconductor manufacturers.
Four-sided I-lead flat package. One of the surface mount packages.
Four-sided J-lead flat package. One of the surface mount packages.
Four-sided leadless flat package. One of the surface mount packages. In the late 1990s, it was often called LCC.
Four-lead flat package. One of the surface-mount packages. The pins are drawn from four sides into a seagull wing (L) shape.
Small center distance from QFP. The name specified by the Japan Electromechanical Industry Association standards.
Another name for ceramic QFP. The name adopted by some semiconductor manufacturers (see QFP, Cerquad).
Another name for plastic QFP. The name adopted by some semiconductor manufacturers (see QFP).
Four-sided pin carrier package. One of the TCP packages. Pins are formed on the insulation tape and lead out from the four sides of the package.
Four-sided pin carrier package. The name used by the Japan Electromechanical Industry Association for the outline specifications of QTCP in April 1993 (see TCP).
Another name for QUIP (see QUIP).
Four-row lead-in package.
Shrinking DIP. One of the plug-in packages, the shape is the same as DIP, and the materials are ceramic and plastic.
Same as SDIP. The name adopted by some semiconductor manufacturers.
Another name for SIP (see SIP). European semiconductor manufacturers mostly use the name SIL.
Single-rank memory module.
56) SIP (single in-line package)
57) SK-DIP (skinny dual in-line package)
A type of DIP. Refers to a narrow body DIP with a width of 7.62mm and a lead center distance of 2.54mm. Commonly referred to as DIP (see DIP).
A type of DIP. Refers to a narrow body DIP with a width of 10.16mm and a lead center distance of 2.54mm. Commonly referred to as DIP.
Surface mount devices. Occasionally, some semiconductor manufacturers classify SOP as SMD (see SOP). Another name for SOP. Many semiconductor manufacturers in the world use this nickname. (See SOP).
Small I-lead package. One of the surface mount packages.
Another name for SOP (see SOP). Many semiconductor manufacturers abroad use this name.
Small J-lead package. One of the surface mount packages.
The name used for the SOP in accordance with JEDEC (United States Electronic Equipment Engineering Council) standards (see SOP).
No heat sink SOP. Same as usual SOP.
Small outline package. One of the surface mount packages, the pins lead out from both sides of the package into a seagull wing shape (L-shaped).
Wide body SOP. The name adopted by some semiconductor manufacturers.
Printed circuit board leadless package. The name adopted by Fujitsu of Japan for plastic QFN (plastic LCC) (see QFN).
