Conventional PCB substrate materials mainly include: phenolic paper-based copper-clad laminate (FR-1, XPC), epoxy fiberglass cloth based copper-clad laminate (FR-4) and its multilayer semi curing sheet, composite base copper-clad laminate (CEM-1, CEM-3). These three kinds of conventional substrate materials have their own characteristics.
1.Comparison of characteristics of three kinds of conventional rigid copper clad laminates:
1).Phenolic paper based copper clad laminate:Phenolic paper-based copper-clad laminate is a kind of insulating layer which is made up of phenolic resin as adhesive and wood pulp fiber paper (some of them are cotton pulp fiber paper) as reinforcement material. The most typical types of such boards are FR-1 (flame retardant) and XPC (non flame retardant). In addition, the type of phenolic paper-based copper clad laminate with slightly higher electrical and mechanical properties is FR-2 (flame retardant).
The properties of phenolic paper-based copper clad laminates are characterized by low cost, low price, small relative density, and punching processing. However, its working temperature is low, and its heat resistance, moisture resistance and mechanical properties are slightly lower than those of epoxy glass fiber cloth based copper clad laminates.
Epoxy glass cloth based copper-clad laminate is an insulating layer with epoxy resin as adhesive and glass fiber cloth as reinforcement material. The most typical types of such boards are FR-4 (flame retardant) and C-10 (non flame retardant). In addition, FR-5 (flame retardant) and C-11 (non flame retardant) are better in heat resistance. The semi-cured sheet and inner core sheet of epoxy glass cloth based copper clad laminate are the important base materials for manufacturing Ordinary multilayer panels.
The mechanical properties, dimensional stability, impact resistance and moisture resistance of epoxy glass fiber cloth based copper clad laminate are higher than those of phenolic paper based copper clad laminate. Its electrical performance is excellent, working temperature is high, its performance is little affected by the environment. Compared with other resin based glass fiber cloth copper clad laminates, it has great advantages in processability.
There are two kinds of composite base copper-clad laminates: flame-retardant copper-clad epoxy glass fiber cloth surface, paper core composite base material laminate (NEMA / ANSI standard model: CEM-1); flame-retardant copper-clad epoxy glass fiber cloth surface, glass fiber paper core composite base material laminate (NEMA / ANSI standard model: cm3). In addition, there are flame-retardant copper-clad polyester glass fiber cloth surface, glass fiber paper core composite base material laminate (model in NEMA / ANSI standard: crm-5).
The composite based copper clad laminate is between epoxy glass fiber cloth based copper clad laminate and phenolic paper based copper clad laminate in mechanical property and manufacturing cost. It can be used for punching or drilling. Some CEM-3 products are superior to FR-4 products in the aspects of CTI resistance, dimensional accuracy and dimensional stability. CEM-1 and CEM-3 have been widely used in Japan, Europe, America and other countries and regions to produce double-sided PCB instead of FR-4.
2.Main application of conventional PCB substrate materials:
The following are the main uses of various types of rigid copper clad laminates and multilayer substrate.
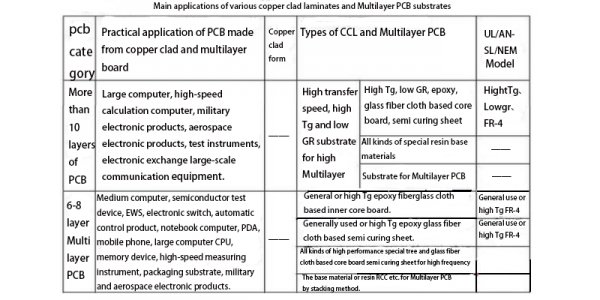
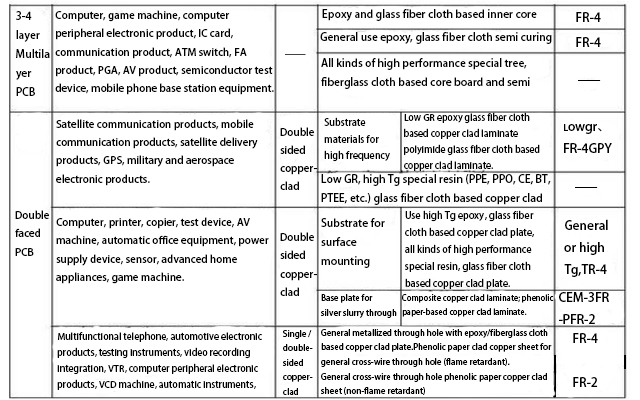
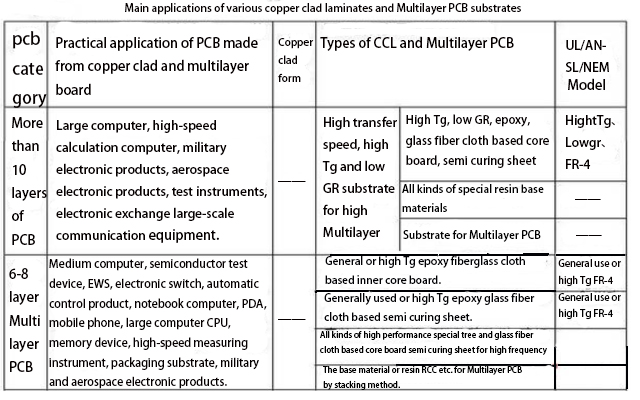
3.Main quality performance of conventional PCB substrate materials:
Some of the quality characteristics of copper clad plate can be expressed directly quantitatively. For example, most of the electrical and mechanical characteristics of copper clad plate; However, some of them cannot be expressed quantitatively directly. In this case, some substitute indicators should be used to express quantitatively indirectly. Such as heat resistance, commonly used copper clad plate after a certain time, a certain temperature or a certain special environment, and then determine its electrical, mechanical properties to express.
The quality characteristics of copper clad sheet are mainly shown in the following aspects:
(1) electrical characteristics. Including insulation, dielectric (dielectric constant, dielectric loss factor, etc.), resistance to ion migration, resistance to leakage trace, resistance to electric field strength, copper foil quality resistance.
(2) mechanical characteristics. Including copper foil and substrate adhesion, mechanical strength (such as bending strength, etc.), impact resistance, dimensional stability, elasticity, thermal deformation, etc.
(3) chemical characteristics. Including heat resistance, glass temperature, weldability, chemical resistance, alkali resistance, acid resistance, water resistance.
(4) physical characteristics. Including thermal expansion coefficient, relative density, flammability (flame retardant), substrate processing, substrate flatness (warp, twist), etc.
(5) environmental resistance. Including mildew resistance, moisture resistance, cooking resistance, heat - resistant cold cycle impact.
(6) environmental characteristics.
The main technical performance indexes of conventional PCB substrate materials are listed in table 2-14 and 2-15. Technical performance indicators for IPC standard (ipc-4101/21) of general type fr-4 board are listed in table 2-14.
Note: the standard technical performance index refers to epoxy glass cloth substrate (fr-4) with vitrification temperature (Tg,TMA at 110-135℃).G plate has the same performance index except for 13 items.
Different characteristics of PCB with different layers:
1). Single-sided PCB:Single-sided Boards are on the most basic PCB, where the parts are centered on one side and the wires on the other (the same side as the wires if there is a patch component, and the plug-in on the other side). Because the wire appears only on one side, this PCB is called single-sided. Because a single panel had many strict restrictions on the design circuit (because there was only one side, the wiring could not cross and they had to go their own way), only early circuits used such boards.
2. Double sided PCB:
Double-sided Boards are Boards that have wiring on both sides, but to use conductors on both sides, you must have proper electrical connections between the two sides. This "bridge" between the circuits is called a guide hole (via). A guide hole is a small hole in a PCB, filled with or coated with metal, that can be connected to wires on both sides. Because the area of the double panel is twice as large as that of the single panel, the double panel solves the problem of interlacing the wiring in the single panel (it can be channeled to the other side through the hole), and it is more suitable for more complex circuits than the single panel.
3. The multilayer PCB:
Multi-layer Boards to increase the area available for wiring, more single - or double-sided wiring Boards are used. With a double lining, two one-way for outer layer or two double lining, two blocks of single outer layer of the printed circuit board, through the positioning system and alternate insulation adhesive materials and conductive graphics interconnection according to design requirement of printed circuit board becomes four, six layer printed circuit board, also known as multilayer printed circuit board. The number of layers of the board does not mean that there are several independent wiring layers. In special cases, an empty layer will be added to control the thickness of the board. Most of the motherboards are four to eight layers, but the technical theory is that you can have up to 100 layers of PCB. Most large supercomputers use quite a few layers of motherboards, but because such computers can be replaced by clusters of many ordinary computers, they are no longer used. Because the layers in the PCB are tightly coupled, it's not always easy to see the actual number, but if you look closely at the motherboard, you can see it.
