Reflow soldering is the most commonly used method of surface mount technology (SMT) for bonding electronic components to printed circuit boards. Another way is to connect electronic components through through-hole insertion (THT). Through-hole insertion is to fill the existing holes on the circuit board with solder paste, insert the pins into the solder paste and embed the electronic components on the board for soldering. Because wave soldering is cheaper and simpler, reflow soldering is basically not used on through-hole circuit boards. When applied to circuit boards containing both SMT and THT components, Through-hole reflow can replace wave soldering and can effectively reduce assembly costs.
The purpose of the reflow soldering process is to gradually melt the solder and slowly heat the connection interface to avoid rapid heating and damage to electronic components. In the traditional reflow soldering process, it is usually divided into four stages, called ‘Zone’, each zone has its own temperature curve and has different effect:
1) Preheat
The heating zone is involved in the first stage of reflow soldering. It preheats and heats the PCB board, heats the solder paste, evaporates a part of the solvent, evaporates and cleans the moisture of the PCB board and components, eliminating the PCB.
2) Insulation
The PCB enters the heat preservation area and reaches a certain temperature to avoid sudden entry into the soldering high temperature area and damage to the PCB and components. The effect of this temperature zone is also to keep the temperature of the component stable, reduce the temperature difference of the entire PCB, evaporating the flux in the solder paste cleanly and removing the oxide of the pad and component pins.
3) Welding
When the PCB enters the soldering zone, the temperature reaches the maximum. At this time, the solder paste has changed from a paste to a liquid, and the pad and component pins are fully wetted. This link has a relatively short duration to avoid damage to the PCB and components at high temperatures.
4) Cooling
After the solder paste transfers into liquid, it can be cooled next. The faster the cooling rate, the better. If the cooling rate is too slow, it is prone to dim roughness. It is generally solidified by cooling to 75 degrees Celsius. At this time, the PCB is completed welded.
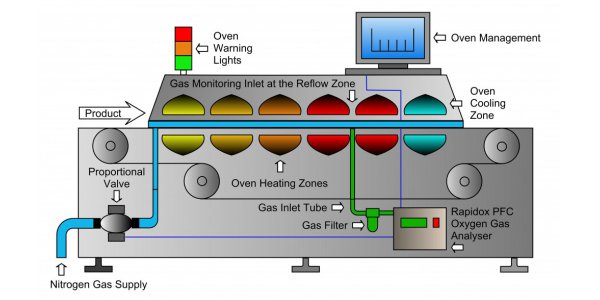
Reflow soldering is the most important process technology in SMT. The quality of reflow soldering is the key to the reliability of SMA. It directly affects the performance reliability and economic benefits of electronic equipment. The welding quality depends on the welding method, welding materials, and welding Process technology and welding equipment. Here are some characteristics of reflow soldering technology:
1) The thermal shock to components is small, but sometimes it will give the device greater thermal stress.
2) Only apply solder paste to the required parts, it can control the amount of solder paste applied and avoid the occurrence of bridges and other defects.
3) The surface tension of the molten solder can correct the slight deviation of the component placement position.
4) A local heating heat source can be used, so that different welding processes are used for welding on the same substrate.
5) Impurities are generally not mixed in the solder. When using solder paste, the composition of the solder can be correctly maintained.
Reflow soldering is to send the mounted circuit board of the chip component into the SMT reflow soldering chamber. After high temperature, the solder paste used to solder the chip component is melted by the process of high temperature hot air forming reflow temperature change, so that the chip component Combine with the pads on the circuit board and then cool them together.
