Posted: May 14, 2022 by: Bonnie
1. Resistance (R)
Definition: It is an electronic component made by using the characteristic of substances to hinder the flow of current. It is one of the most basic and commonly used electronic components in electronic products.
Function: The resistance itself has an obstructive effect on the current, and it can be used in the circuit according to the different forms of the circuit. The main functions are current limiting, pressure reduction, partial pressure, bias, etc.
Classification: ordinary resistance, sensitive resistance, variable resistance
Ordinary resistance: It is a kind of resistance with fixed resistance. According to different manufacturing processes and functions, the previous ones will be classified in detail.
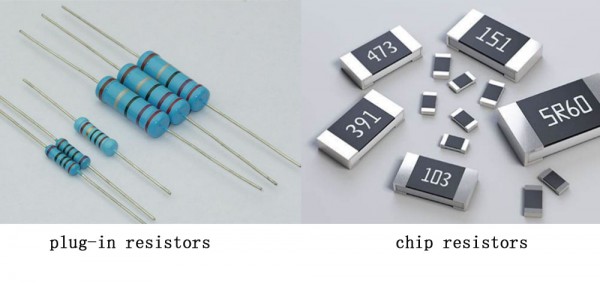
Main resistance: plug-in resistors, chip resistors
Sensitive resistance: refers to the size of its resistance that can be changed by changes in the external environment (such as temperature, humidity, brightness, voltage, etc.), so it is often used in some sensors.
Mainly divided into thermistor, photoresistor, humidity-sensitive resistor, varistor, gas-sensitive resistor.

2. Capacitance (C)
Definition: It is a component that can store electrical energy. Almost every electronic product has a capacitor.
Function: The capacitor has the characteristics of blocking DC and communicating with AC. The main functions are filtering, coupling, timing, decoupling, tuning loop, energy conversion, control, etc.
Classification: ordinary capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, variable capacitors
Ordinary capacitors: color ring capacitors, ceramic capacitors, polyester capacitors, etc.

Electrolytic capacitor: The pin has a clear distinction between positive and negative, so it is also called a polarized capacitor. When using this type of capacitor, the polarity of the two pins cannot be reversed.
Mainly: aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum electrolytic capacitors
Variable capacitance: The capacitance can be adjusted within a certain range, and is mainly used to select signals in the radio receiving circuit.
3. Inductance (L)
Definition: It belongs to an energy storage element that can convert electrical energy into magnetic energy and store it. The inductance presents a small resistance to DC (approximately a short circuit) and a high impedance to AC. The magnitude of its resistance is related to the frequency of the passed AC signal. The same inductance element, the higher the frequency of the alternating current, the greater the resistance.
The application of inductors is very wide, and indifferent electronic products, the types of inductors used are different according to different application environments.
Function: Mainly have the functions of filtering, resonance, etc. It is mainly connected with capacitors in series and parallel to form an LC series and parallel resonance circuit, which screens signals, stabilizes current, and suppresses electromagnetic wave interference.
Classification: Color ring inductors, inductor coils, chip inductors, fine-tuning inductors
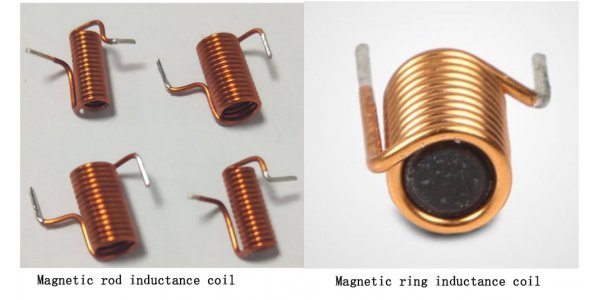
Inductance coil: air-core inductance coil, magnetic rod inductance coil, magnetic loop inductance coil, choke coil.
4. Diode (D)
Definition: A diode is a semiconductor device with a PN junction. The inside is composed of a P-type semiconductor and an N-type semiconductor. The corresponding electrode leads are drawn at both ends of the PN junction, and the tube case is sealed to make a diode.
Function: The diode has unidirectional conductivity, and its main functions are: AC rectification, power supply voltage stabilization, modulation signal detection, amplitude limiting, and clamping, etc.
Classification: Schottky diodes, rectifier diodes, Zener diodes, light-emitting diodes, photodiodes, detector diodes, varactor diodes, etc.
5. Transistor (QTR)
Definition: The full name of a triode is a transistor, which is a semiconductor device with amplifying function.
Function: The triode is a current amplifying electrical device, which can be made into an AC or DC signal amplifier, and it also has functions such as switches.
Structure classification: NPN type and PNP type triode
Function classification: switch tube, power tube, Darlington tube, photosensitive tube
6. Transistor
Definition: Transistor generally refers to all single components based on semiconductor materials, including diodes (two-terminal), triode, field-effect transistor, thyristor (the latter three are three-terminal) made of various semiconductor materials. The Transistor is sometimes referred to as a transistor.
Function: The transistor has a fast response speed and high accuracy. The transistor can be used for a variety of digital and analog functions, including amplification, switching, voltage stabilization, signal modulation, and oscillators.
Classification: Bipolar Transistor (BJT), Field Effect Transistor (FET), Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
Junction field-effect transistors are generally used in differential input circuits of audio amplifiers and circuits such as modulation, amplification, impedance conversion, current stabilization, current limiting, and automatic protection.
Field-effect transistor
Insulated gate field-effect transistors are often used in circuits such as audio power amplifiers, switching power supplies, inverters, power converters, ballasts, chargers, motor drives, and relay drives.
7. Thyristor (V, VT)
Definition: Thyristor is the abbreviation of thyristor, which is a kind of controlled rectifier device, also known as a thyristor. Under certain voltage conditions, the thyristor can be turned on as long as there is a trigger pulse, and the trigger pulse disappears, and the thyristor can still maintain the conductive state.
Classification: unidirectional thyristor, bidirectional thyristor, single thyristor, turn-off thyristor, etc.
Function: Thyristor is a very important power device. Its main feature is to realize high voltage and high current control through a small current. Main function: As a controllable rectifier device, as a controllable electronic switch.
8. Sensor
Definition: A detection device that can feel the information to be measured, and can transform the sensed information into electrical signals or other required forms of information output according to a certain rule, so as to satisfy the transmission, processing, storage, and display of information, Recording and control requirements.
Function: The function of the sensor is similar to that of human sensory organs, and it is the primary link to realize automatic detection and automatic control. The role of the sensor is actually a functional block, its role is to convert various signals from the outside into electrical signals.
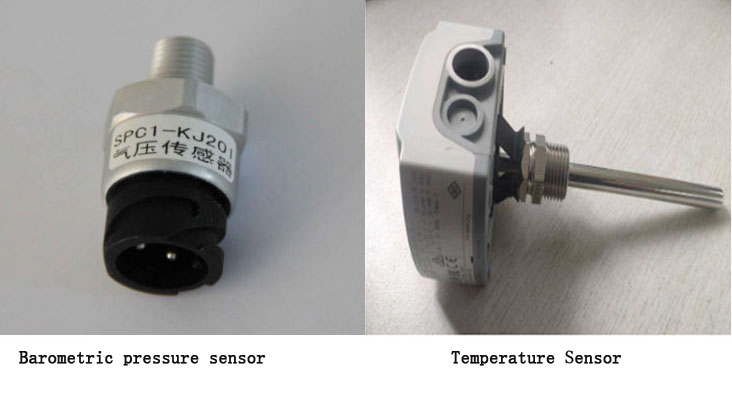
Classification: pressure sensor, gas sensor, temperature sensor, position sensor, speed sensor, acceleration sensor
9. Transformer
Definition: A transformer is a device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to change the current. The main components are the primary coil, the secondary coil, and the iron core (magnetic core). A transformer is a device that transforms voltage, current, and impedance. When an alternating current is passed through the primary coil, an alternating magnetic flux is generated in the iron core (or magnetic core), which induces a voltage (or current) in the secondary coil.
Function: The transformer is mainly used for AC voltage conversion, current conversion, power transfer, impedance conversion, and buffer isolation, etc. It is one of the indispensable important components of the PCBA machine.
Classification: power transformers, voltage regulating transformers, audio transformers, pulse transformers, etc.
10. Crystal oscillator (X, G, Z)
Definition: The crystal oscillator generally refers to the vigilant oscillator, which refers to the slice (referred to as the wafer) cut from a quartz crystal at a certain azimuth angle, and the crystal element that adds the IC to form the oscillator circuit inside the package is called the crystal oscillator. Its products are generally packaged in metal shells, but also glass, ceramic or plastic packages.
Function: The crystal oscillator uses a crystal that can convert electrical energy and mechanical energy into each other. It can provide stable and accurate single-frequency oscillation when working in a resonance state. Provide the basic clock signal for the system. Usually, a system shares a crystal oscillator to facilitate the synchronization of all parts.
Classification: Oven crystal oscillator, temperature compensated crystal oscillator, ordinary crystal oscillator, voltage-controlled crystal oscillator

11. Connector
Definition: Generally refers to electrical connectors. That is, a device that connects two active devices to transmit current or signal. The connector is a component that electronic engineering and technical personnel often touch.
Function: Build a bridge of communication between the blocked or isolated circuits in the circuit, so that the current can flow, and the circuit can realize the predetermined function. The main functions are the internal connection of the chip package, the connector IC socket, the printed circuit PCB connector, and the interconnection between devices.
Classification: general connector, moisture-proof and waterproof connector, air-tight connector, fire-resistant connector, etc.
12. Interface chip
Definition: An interface chip is a chip with an interface circuit inside
function:
(1) Set data registration and buffer logic to adapt to the speed difference between CPU and peripherals. The interface is usually composed of some registers or RAM chips. If the chip is large enough, it can also realize the transfer of bulk data;
(2) Data conversion function: can convert information format, such as serial and parallel conversion;
(3) Three-state buffer function: coordinate timing differences;
(4) Address decoding and equipment selection functions;
(5) Set up the interrupt and DMA control logic to ensure that the interrupt and DMA request signal is generated when the interrupt and DMA are allowed, and complete the interrupt processing and DMA transmission after receiving the interrupt and DMA response.
Classification: USB chip, JTAG interface chip, UART interface chip, USB transceiver, CNA chip, etc.
13. Memory chip
Definition: It is the specific application of the concept of embedded system chip in the storage industry. Whether it is a system chips or a storage chip, it is achieved by embedding software in a single chip to achieve multi-function and high performance, as well as for multiple protocols and multiple hardware And support for different applications.
Function: The storage chip can quickly realize the integration of various storage functions into a single chip to ensure the high performance of the optimized system. Provide high-quality support for access performance, storage protocols, management platforms, storage media, and a variety of applications.
Contains: Flash chip, EEPROM chip, PROM chip, RAM chip, XOR gate chip

14. Sequential logic circuit
Definition: Sequential logic circuit is that the output at any moment not only depends on the input signal at that time but also depends on the original state of the circuit, in other words, it is also related to the previous input.
Contains counters, registers, FIFOs, D flip-flops, latches, frequency dividers, etc.
15. Processor unit
Definition: The processor unit consists of several components, including CPU (central processing unit), MPU (microprocessor), DSP (digital signal processor), microcontroller, development board, SBC (single board computer), and other devices.
In PLC, the processor is the "brain" with a decision-making function, and it controls the operation of the components connected to it. The processor controls the output device connected to the output module according to the input state of the input device and the program solidified in the PLC memory.
16. Electronic display
Definition: Refers to an information display device that uses electronic technology to turn an imperceptible signal into a perceptible signal. It has the advantages of small space occupation, flexible and variable display format, and the ability to comprehensively display a variety of information at the same time.
Classification: Dot matrix display, LCD display, active matrix display, OLED display, etc.
Dot-matrix display
There are many more components that need to be used in PCBA patch processing. The above is only a part. For more details, you can go to FindIC (FindIC) to inquire in detail.
FindIC (FindIC) is China's largest electronic component search engine, providing 200 million component quotations online, and automatically matching BOM model, brand, price, inventory, and other data in 10 seconds. Include 8000W+ product data manual, 13000+ domestic and foreign chip manufacturers, daily update data 3 million+, real-time update of global electronic component inventory, prices and specifications, and other information.
The performance and quality of electronic components affect the quality of PCBA finished products, so it is very important to understand the function of each component in detail.
