Electronic Assembly Process Reliability Screening
Posted: May 14, 2022
By: Bonnie
According to the production and use of electronic products, reliability screening can be divided into finished product screening, process screening of device production lines and screening before use of the whole machine factory. The following is a brief introduction to some commonly used screening methods.
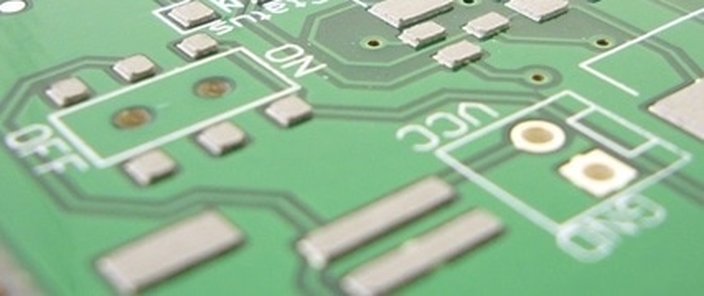
1. Visual inspection and microscopic screening
An important screening method in the manufacture of electronic products during visual inspection or microscopy (microscopy). It can be used to detect and eliminate stains, defects, damage and poor connections. The microscopic inspection standard should be reasonably formulated according to the main failure mode and mechanism, combined with the specific failure process conditions. Years of experience have recognized this approach as one of the easiest and most efficient methods. It is effective for inspecting various defects on the surface of the chip (such as metallization layer defects, chip cracks, oxide layer quality, mask quality and diffusion defects, etc.) as well as observing inner lead stitching, chip soldering, and package defects. Automated microscopy systems using scanning electron microscopes combined with computers have been used abroad.
2. X-ray screening
X-rays are non-destructive screenings used to inspect the device for leaks, check for potential defects in the package, bonding and packaging defects, and cracks on the chip.
3. Infrared screening
Thermal distribution characteristics (hot spots and hot spots) are revealed by infrared detection or photographic techniques. When the design is unreasonable, there are defects in the process, and there are some failure mechanisms in the production process, hot spots or hot spots will be generated in a certain part of the product. This pre-screens out unreliable components. The advantage of infrared screening is that it does not damage components during the inspection process, and is especially suitable for inspection of large-scale integrated circuits.
4. Power aging
Power aging is a very effective screening method and one of the screening methods that high integrated circuits must perform. Power aging is eliminated by applying an electrical stress to the product that causes potential defects in the early failed device to be exposed as quickly as possible. It can effectively eliminate process defects, thin metal film and scratches and surface contamination in the production process of the device. Power aging is usually to place the integrated circuit product under high temperature conditions, apply the maximum voltage to obtain a large enough screening stress, to eliminate the early failure of the product under high temperature conditions, apply the maximum voltage to obtain a sufficiently large pulse power. Ageing. The former is mostly used for small-scale digital circuits, while the latter is used for medium and large-scale integrated circuits, so that the components in the circuit can withstand the maximum power consumption and stress under working conditions when aging. Although ultra-power aging shortens the aging time, it is also possible to cause the instantaneous load of the device to exceed the maximum rated value, causing damage to the qualified device and even immediate deterioration or breakdown. Some products may work temporarily, but their lifespan is shortened. Therefore, for super power aging, it is not the more super and the more effective, but should choose the best overload. The more consistent method is to apply the maximum rated power to the device and prolong the aging time. It is a reasonable method for screening the electric power aging.
5. Temperature cycling and thermal shock screening
Temperature cycling accelerates failure due to thermal mismatch between materials. Potential defects such as chip assembly, bonding, encapsulation, and metallization of the oxide layer can be screened by temperature cycling. Typical conditions for temperature cycling screening are -55 to +155 ° C or -65 to +200 ° C for 3 or 5 cycles. Each cycle was maintained at the highest or lowest temperature for 30 min each and the transfer time was 15 min. After the test, the AC and DC parameters were tested. Thermal shock screening is an effective method for determining the strength of an integrated circuit with a sharp temperature change. For example, two water tanks of 100 ° C and 0 ° C are provided, which are taken out after immersion in a high temperature bath for 15 s, and moved into a low temperature tank for at least 5 s in 3 s, and then immersed for at least 5 s. Move into the high temperature tank. This is reciprocated 5 times. For some products, if the thermal expansion and contraction performance of the internal parts of the material does not match, or the parts have cracks, or defects caused by poor SMT process, the early failure parts can be advanced in the high temperature and low temperature alternating environment temperature impact. Invalid. This method has a good screening effect.
6. High temperature storage screening
High temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions inside the product. If water vapor or various harmful gases are contained in the envelope of the integrated circuit package, or the surface of the chip is not clean, or there are various metal components at the bonding site, a chemical reaction occurs, and high temperature storage accelerates these reactions. Because this screening method is easy to operate, it can be carried out in batches, the screening effect is good, and the investment is small, so the application is more common.
7. High temperature work screening
High-temperature work screening generally has high-temperature DC static, high-temperature AC dynamics and high-temperature reverse bias 3 screening methods, which is very effective in eliminating the defects caused by potential defects in the surface, body and metallization system of the device. High-temperature reverse bias is a test of adding reverse-bias working voltage at high temperature. It is carried out under the joint action of hotspots, which is close to the actual working state, so it is better than pure high-temperature storage screening.

SMT Reliability Screening
1. Visual inspection and microscopic screening
An important screening method in the manufacture of electronic products during visual inspection or microscopy (microscopy). It can be used to detect and eliminate stains, defects, damage and poor connections. The microscopic inspection standard should be reasonably formulated according to the main failure mode and mechanism, combined with the specific failure process conditions. Years of experience have recognized this approach as one of the easiest and most efficient methods. It is effective for inspecting various defects on the surface of the chip (such as metallization layer defects, chip cracks, oxide layer quality, mask quality and diffusion defects, etc.) as well as observing inner lead stitching, chip soldering, and package defects. Automated microscopy systems using scanning electron microscopes combined with computers have been used abroad.
2. X-ray screening
X-rays are non-destructive screenings used to inspect the device for leaks, check for potential defects in the package, bonding and packaging defects, and cracks on the chip.
3. Infrared screening
Thermal distribution characteristics (hot spots and hot spots) are revealed by infrared detection or photographic techniques. When the design is unreasonable, there are defects in the process, and there are some failure mechanisms in the production process, hot spots or hot spots will be generated in a certain part of the product. This pre-screens out unreliable components. The advantage of infrared screening is that it does not damage components during the inspection process, and is especially suitable for inspection of large-scale integrated circuits.
4. Power aging
Power aging is a very effective screening method and one of the screening methods that high integrated circuits must perform. Power aging is eliminated by applying an electrical stress to the product that causes potential defects in the early failed device to be exposed as quickly as possible. It can effectively eliminate process defects, thin metal film and scratches and surface contamination in the production process of the device. Power aging is usually to place the integrated circuit product under high temperature conditions, apply the maximum voltage to obtain a large enough screening stress, to eliminate the early failure of the product under high temperature conditions, apply the maximum voltage to obtain a sufficiently large pulse power. Ageing. The former is mostly used for small-scale digital circuits, while the latter is used for medium and large-scale integrated circuits, so that the components in the circuit can withstand the maximum power consumption and stress under working conditions when aging. Although ultra-power aging shortens the aging time, it is also possible to cause the instantaneous load of the device to exceed the maximum rated value, causing damage to the qualified device and even immediate deterioration or breakdown. Some products may work temporarily, but their lifespan is shortened. Therefore, for super power aging, it is not the more super and the more effective, but should choose the best overload. The more consistent method is to apply the maximum rated power to the device and prolong the aging time. It is a reasonable method for screening the electric power aging.
5. Temperature cycling and thermal shock screening
Temperature cycling accelerates failure due to thermal mismatch between materials. Potential defects such as chip assembly, bonding, encapsulation, and metallization of the oxide layer can be screened by temperature cycling. Typical conditions for temperature cycling screening are -55 to +155 ° C or -65 to +200 ° C for 3 or 5 cycles. Each cycle was maintained at the highest or lowest temperature for 30 min each and the transfer time was 15 min. After the test, the AC and DC parameters were tested. Thermal shock screening is an effective method for determining the strength of an integrated circuit with a sharp temperature change. For example, two water tanks of 100 ° C and 0 ° C are provided, which are taken out after immersion in a high temperature bath for 15 s, and moved into a low temperature tank for at least 5 s in 3 s, and then immersed for at least 5 s. Move into the high temperature tank. This is reciprocated 5 times. For some products, if the thermal expansion and contraction performance of the internal parts of the material does not match, or the parts have cracks, or defects caused by poor SMT process, the early failure parts can be advanced in the high temperature and low temperature alternating environment temperature impact. Invalid. This method has a good screening effect.
6. High temperature storage screening
High temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions inside the product. If water vapor or various harmful gases are contained in the envelope of the integrated circuit package, or the surface of the chip is not clean, or there are various metal components at the bonding site, a chemical reaction occurs, and high temperature storage accelerates these reactions. Because this screening method is easy to operate, it can be carried out in batches, the screening effect is good, and the investment is small, so the application is more common.
7. High temperature work screening
High-temperature work screening generally has high-temperature DC static, high-temperature AC dynamics and high-temperature reverse bias 3 screening methods, which is very effective in eliminating the defects caused by potential defects in the surface, body and metallization system of the device. High-temperature reverse bias is a test of adding reverse-bias working voltage at high temperature. It is carried out under the joint action of hotspots, which is close to the actual working state, so it is better than pure high-temperature storage screening.
More resources:
Do you have any questions about the above-mentioned? Contact us now, we will reply to you soon.
Is the article useful to you?
No
Yes(
11
)
11
540
1
Share to:
