Characteristic impedance is a concept in the range of VHF and UHF. It is not a DC resistance. It belongs to the concept of long line transmission. In the process of signal transmission, there will be a transient current between the signal line and the reference plane (power plane or ground plane) due to the establishment of electric field. If the transmission line is isotropic, as long as the signal is transmitted, there will always be a current I. if the output level of the signal is V, then in the process of signal transmission( Note that in the transmission process), the transmission line will be equivalent to a resistance with the size of V / I, we call this equivalent resistance the characteristic impedance (z) of the transmission line.
It should be noted that this characteristic impedance is for AC signal, and for DC signal, the resistance of transmission line is far less than Z, rather than Z. In the process of signal transmission, if the characteristic impedance of the transmission path changes, the signal will reflect at the node with discontinuous impedance.The basic characteristics of transmission line are characteristic impedance and signal transmission delay. Here, we mainly discuss characteristic impedance. Transmission line is a distributed parameter system, each section of which has distributed capacitance, inductance and resistance. The distribution parameters of transmission lines are usually expressed by inductance L and capacitance C per unit length, as well as resistance and conductance per unit length. They are mainly determined by the geometry of transmission lines and the characteristics of insulating media. Distributed capacitance, inductance and resistance are inherent parameters of transmission lines. Given a certain transmission line, the values of these parameters are determined. These parameters reflect the internal factors of transmission lines, and their existence determines a series of important characteristics of transmission lines.

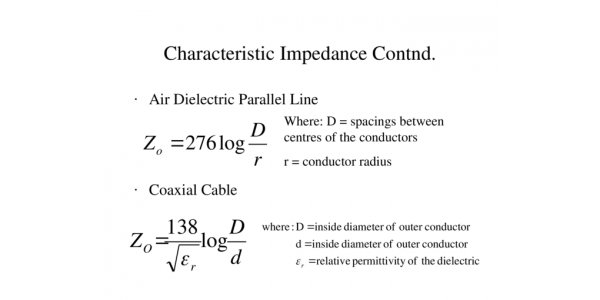
The formula for calculating the characteristic impedance is Z0= 87/ SQRT (Er+1.41) x 1n [5.98 h/ (0.8w+t)], Z0 represents the characteristic impedance of printed wire, Er represents the dielectric constant of the insulating material, h represents the thickness of the medium between the printed wire and the reference plane, w represents the width of the printed wire and t represents the thickness of the printed wire. Z0 describes the characteristic impedance of the transmission line, but it is described under the condition of no loss. The thermal loss and dielectric loss on the resistance are ignored, that is, the voltage waveform distortion caused by DC voltage change and leakage is not taken into account. In practical application, it must be analyzed concretely.
Nowadays,fast switching speed or high clock rate PCB traces must be considered as transmission lines. Transmission lines can be divided into single ended (unbalanced) transmission lines and differential (balanced) transmission lines.Single ended transmission lines are the most common way to connect two devices. When a wire connects the source of one device to the load of another, and the reference (ground) layer provides the signal loop. When the signal jumps, the current in the current loop also changes. It will cause the voltage drop of the ground circuit, which will constitute the noise source of other single ended transmission line receivers in the system, so as to reduce the noise tolerance of the system.
