Designers need to understand the performance characteristics of BGAs, which are similar to earlier SMDs. The PCB designer must know how to modify the design accordingly when the manufacturing process changes. For manufacturers, they face the challenge of dealing with different types of BGA packages and changes in the final process. To increase yield, assemblers must consider establishing a new standard for handling BGA devices. Finally, perhaps the key to getting the most cost-effective assembly is with BGA reworkers.
The third type of BGA package is the tape carrier grid package (TBGA), which is increasingly used in high-performance components that require lighter and thinner devices. On a polyimide carrier tape, the TBGA's I / O leads can exceed 700. TBGA can be processed using standard screen-printed solder paste and traditional infrared reflow soldering methods.
1. Characteristics of BGA soldering
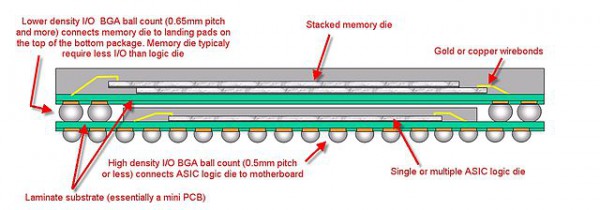
BGA ball grid array package: With the development of integrated circuit technology in PCBA boards, the packaging requirements for integrated circuits have become more stringent. This is because the packaging technology is related to the functionality of the product. When the frequency of the IC exceeds 100MHz, the traditional packaging method may produce a so-called "CrossTalk" phenomenon. When the IC pin number is greater than 208 Pins, the traditional packaging method is difficulty. Therefore, in addition to using QFP packaging, most high-pin count chips today use BGA (Ball Grid Array Package) packaging technology. As soon as BGA appeared, it became the best choice for VLSI chips such as CPU, and high-density, high-performance, high I / O pin packages such as south / north bridge chips on the motherboard. Its characteristics are:1. Although the number of I / O pins is increased, the pin pitch is much larger than QFP, which improves the assembly yield.
2. Although its power consumption increases, the BGA can be soldered by a controlled collapsed chip method, referred to as C4 soldering, which can improve its electrical and thermal performance.
3.Thickness is reduced by more than 1/2 than QFP, and weight is reduced by more than 3/4
4. The parasitic parameters are reduced, the signal transmission delay is small, and the frequency of use is greatly increased.
5. Assembly can be coplanar welding, high reliability
6.BGA package is still the same as QFP and PGA, taking up too much substrate area
Intel Corporation has a high level of integration (up to 3 million transistors in a single chip) and CPU chips with high power consumption, such as Pentium, Pentium Pro, and Pentium Ⅱ. Ceramic pin grid array packages CPGA and ceramic ball grid array packages are used. CBGA, and install a micro exhaust fan on the shell to dissipate heat, so as to achieve stable and reliable operation of the circuit.
2. BGA soldering issues
The big advantage of BGA soldering is that if the assembly method is correct, its pass rate is higher than traditional devices. This is because it has no leads, which simplifies the handling of components and therefore reduces the possibility of damage to the device.The BGA reflow process is the same as the SMD reflow process, but BGA reflow requires precise temperature control and an ideal temperature profile for each component. In addition, most BGA devices are automatically aligned on the pad during reflow. Therefore, from a practical point of view, BGAs can be assembled with equipment for assembling SMD.
However, since the solder joints of the BGA are invisible, it is necessary to carefully observe the application of the solder paste. The accuracy of solder paste application, especially for CBGA, will directly affect the assembly qualification rate. SMD device assembly is generally allowed to have a low pass rate because it is fast and cheap to rework, but BGA devices do not have such advantages. To improve the initial pass rate, many assemblers of high-volume BGAs have purchased inspection systems and complex repair equipment. Inspection of solder paste application and component placement before reflow can reduce costs more than inspection after reflow, because inspection is difficult after reflow, and the required equipment is expensive.
Careful selection of solder paste is required because the composition of solder paste is not always ideal for BGA assembly, especially for PBGA assembly. Suppliers must be assured that their solder paste does not form solder joint cavities. Also, if using water-soluble solder paste, care should be taken in selecting the package type.
Because PBGA is sensitive to moisture, pretreatment measures must be taken before assembly. It is recommended that all packages be fully assembled and reflowed within 24 hours. Too long a device leaves the antistatic protective bag will damage the device. CBGA is not sensitive to moisture, but care must be taken.
3. Will the solder mask printing offset of the circuit board cause a BGA short circuit?
Because the PCB becomes smaller and smaller, the associated requirements for the solder mask size are also relatively reduced, which may cause the solder mask printing offset to exceed the solder pad. So, what problems does the solder mask printing offset cause?If the BGA pad is offset, it will cause the BGA solder ball pad to become smaller, and finally cause a solder short. How can the pad become smaller and cause a short circuit? It turns out that the opening on the stencil is fixed, that is, the amount of solder paste in the same opening on the stencil is theoretically fixed. If the size of the BGA pads on each circuit board are the same, the stencil can be appropriate according to the actual pad size. The size of the openings and the amount of solder paste, but if different batches of circuit boards, some pads remain the same size, but some board pads have been reduced, but the amount of solder paste remains the same, too much solder paste caused overflow .. In severe cases, it will overflow to the adjacent pads, forming a solder short.
But how can the pads get smaller?
The Solder Mask will cover the copper foil and wiring that do not need to be exposed on the circuit board to avoid unnecessary contact, short circuit or oxidation. Assume that the circuit board design sets the tolerance of the solder mask to +/- 1mil (+/- 0.0254mm), but the process capability of the factory solder mask is +/- 2mils (+/- 0.05mm), so the solder mask layer is actually printing deviation. It will cover the pads that should have been exposed, making the pads that should have been exposed smaller, so the above problems occur. Another reason is that in order to prevent HIP (Head-In-Pillow), we printed more solder paste on the outer ring of the BGA, so the short-circuited solder pads are mostly concentrated on the outer ball of the BGA.
