Flexible PCB with the quality of light, thin thickness, flexible bending and folding, and other fine characteristics... However, the quality inspection of FPC in China mainly relies on manual visual inspection, with high cost and low efficiency. With the rapid development of the electronic industry, the circuit board design tends to be more and more high-precision and high-density, and the traditional manual detection method has been unable to meet the production demand, so the automatic detection of FPC defects has become an inevitable trend in the development of the industry.
1). Insulation film:
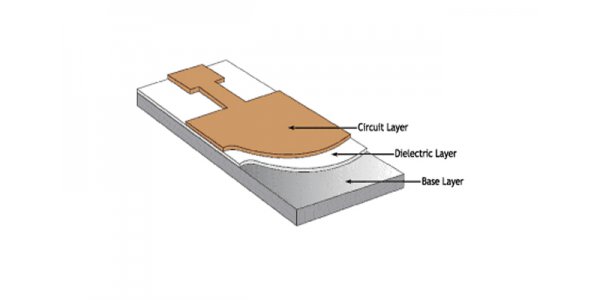
The insulation film forms the base layer of the circuit, and the adhesive attaches the copper foil to the insulation layer. In a multilayer design, it is then bonded to the inner layer. They are also used as a protective covering to insulate the circuit from dust and moisture and to reduce stress during deflection. Copper foil forms a conductive layer.
In some flexible circuits, rigid members made of aluminum or stainless steel provide dimensional stability, physical support for the placement of components and wires, and stress relief. The adhesive binds the rigid member to the flexible circuit. Another material that is sometimes used in flexible circuits is the bonding layer, which is formed by coating the sides of an insulating film with an adhesive. Bonding laminates provide environmental protection and electronic insulation, and the ability to eliminate a single layer of film, as well as multiple layers with fewer bonding layers.
There are many types of insulating film materials, but the most commonly used are polyimide and polyester materials. Nearly 80 percent of all flexible circuit manufacturers in the United States use polyimide film materials, and about 20 percent use polyester film materials. Polyimide materials have a flammability, stable geometrical dimension and has high resistance to tear strength, and have the ability to withstand the welding temperature, polyester, also known as polyethylene double phthalates (Polyethyleneterephthalate referred to as: PET), its physical properties similar to the polyimide, have lower dielectric constant, absorption of moisture is very small, but not resistant to high temperature. The melting point of polyesters is 250 ° c and the glass conversion temperature (Tg) is 80 ° c, which limits their use in applications where extensive end welding is required. They are rigid for low temperature applications. Nevertheless, they are suitable for use in products such as phones and others that do not require exposure to harsh environments. Polyimide insulation film is usually combined with polyimide or acrylic acid adhesive, polyester insulation materials are generally combined with polyester adhesive. The advantage of combining with materials with the same properties can be the dimensional stability after dry welding or after multiple lamination cycles. Other important properties in adhesives are lower dielectric constant, higher insulation resistance, higher glass conversion temperature, and lower moisture absorption.
1.The conductor:
Copper foil is suitable for use in flexible circuits, it can use the electric deposition (Electrodeposited, ED.), or plating system. Electrodeposited copper foil has a shiny surface on one side, while the processed surface on the other side is dull and dull. It is a flexible material that can be made into many thicknesses and widths, and the dull side of ED copper foil is often specially treated to improve its bonding ability. Forged copper foil not only has flexibility, but also has the characteristics of hard and smooth, which is suitable for application in the case of dynamic deflection.
2. Adhesives:
In addition to being used to bond insulating films to conductive materials, adhesives can also be used as a covering, as a protective coating, and as a covering coating. The main difference between the two is in the way they are applied. Screen printing technique used for coating of adhesive. Not all lamination structures contain adhesives, and lamination without adhesives results in thinner circuits and greater flexibility. Compared with the lamination structure based on adhesive, it has better thermal conductivity. It can be used in the working environment where the flexible circuit based on the adhesive lamination structure cannot be used due to the thin structure characteristics of the flexible circuit without adhesive and the improved thermal conductivity due to the elimination of the thermal resistance of the adhesive.
Aluminum pcb definition:
The printed circuit board made of aluminum core material is called aluminum PCB, which is commonly used in LED lighting products due to its strong heat dissipation capacity. The front and the back have two sides. The white side is welded to the LED pin and the other side is in aluminum form. Usually, apply a thermal paste and then make contact with the thermal section.
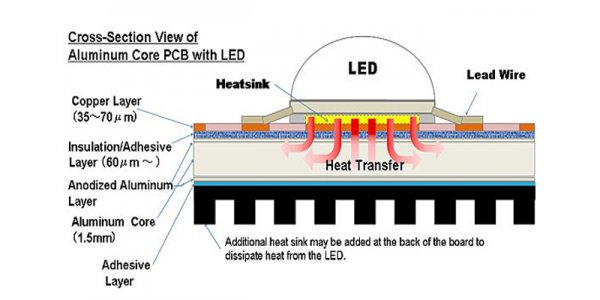
Example of the role of aluminum PCB in LED:
Aluminum substrate is a metal base copper clad laminate with good heat dissipation function. Typically, a single-sided aluminum PCB consists of three layers, the circuit layer (copper foil), the insulation layer, and the metal base. Also used for high-end applications designed for both sides, the structure is circuit layer, insulation layer, aluminum base, insulation layer, circuit layer. Very few applications are laminates, which can be composed of ordinary laminates combined with insulation and aluminum substrates.
LED aluminum substrate is PCB, which also means printed circuit board. The circuit board is made of aluminum alloy. In the past, the material of our general circuit board is glass fiber, but because of the great heat of LED, the circuit board of LED lamp is usually aluminum substrate can conduct heat quickly, other equipment or electrical circuit board is still glass fiber board!