1. Introduction
The emergence and development of FPC and PCB have promoted a new product of soft and hard board. Therefore, Rigid Flex PCB, the flexible circuit board and the rigid circuit board, after pressing and other processes, combined according to the relevant process requirements, to form a circuit board with FPC characteristics and PCB characteristics.
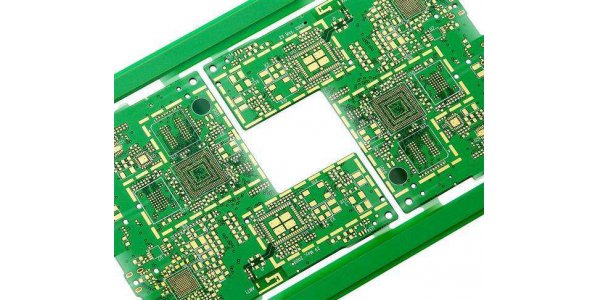
2. Manufacturing process
Because the rigid-flex board is a combination of FPC and PCB, the production of the rigid-flex board should have both FPC production equipment and PCB production equipment. First, the electronic engineer draws the circuit and shape of the flexible bonding board according to the demand, and then sends it to the factory that can produce the flexible and rigid bonding board. After the CAM engineer processes and plans the relevant documents, then arranges the FPC production line production station FPC and PCB production lines are required to produce PCB. After these two flexible boards and hard boards come out, according to the planning requirements of electronic engineers, FPC and PCB are seamlessly pressed by a pressing machine, and then go through a series of details. It became a hard and soft board. It is a very important part, because the hard and soft combination board is difficult and has many details. Before shipment, it is generally necessary to carry out a full inspection, because its value is relatively high, so as not to cause the supply and demand sides to cause related losses of interest.
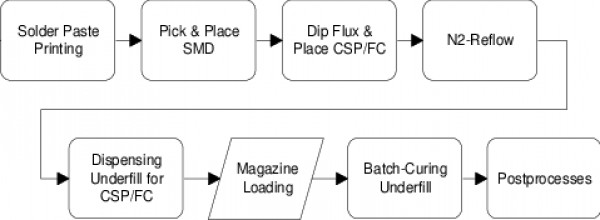
3. Process flow
1)Selection of materials
2) Production process and control of key parts
-Production process
-Graphic transfer of inner monolithic
-Multi-layer positioning of flexible materials
-Laminated
-Drilling
-Decontamination and erosion
-Chemical copper plating, copper plating
-Surface solder mask and solder-ability protection layer
-Outline processing
4. Application
1) Industrial use: Industrial use includes the rigid and flexible boards used in industry, military and medical treatment. Most industrial parts require precise, safe, and non-destructive soil. Therefore, the characteristics required for rigid and flexible boards are: high reliability, high precision, low impedance loss, complete signal transmission quality, and durability. But because of the complexity of the process, the output is small and the unit price is quite high.
2) Mobile phone: The application of soft and hard boards in mobile phones, common ones are the turning points of folding mobile phones (Hinge), camera module (camera Module), button (keypad) and RF module (RF Module).
3) Consumer electronics products: Consumer products, with DSC and DV as the representative of the development of soft and hard boards, can be divided into two main axes of performance and structure to discuss. In terms of performance, the hard and soft boards can connect different PCB hard boards and components in three dimensions, so the total area of the PCB can be increased at the same line density, which can relatively increase the circuit carrying capacity and reduce the signal transmission limit of the contacts. Assembly error rate. On the other hand, since the hard and soft boards are light and thin and can flex the wiring, they have a substantial benefit in reducing the volume and weight.
4) Automobiles: The use of hard and soft boards in automobiles, commonly used are buttons on the steering wheel to connect to the motherboard, connection of the car's video system screen and control panel, operation connection of the audio or function keys on the side door, reversing radar imaging system , Sensor (sensor, including air quality, temperature and humidity, special gas adjustment, etc.), vehicle communication system, satellite navigation, rear seat control panel and front controller connection board, outside vehicle detection system, etc.
